Ceilometer 源码学习 - Notification Agent
简介
Ceilometer有两种数据收集方式,Ceilometer 源码学习 - Polling Agent中提到了主动调用api的Polling方式。显而易见的,这种方式会增加其他组件的负担。所以更优雅也是更推荐的方式是由Notification Agent监听消息队列并收集需要的数据。 这篇文章就将介绍Notification Agent的功能和实现。
需求导向
一句话来概括Notification Agent的功能:
监听消息队列上其他Openstack组件产生的通知数据,加工处理后将数据发送出来
结构图如下: 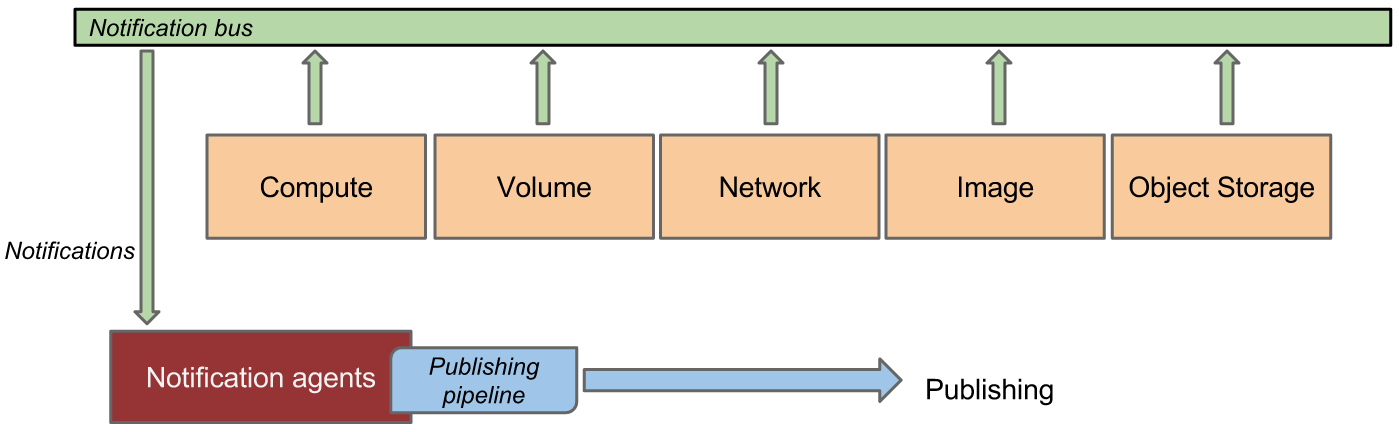
可以看出Notification Agent中需要完成下面这些事情:
- 监听消息队列,收集数据;
- 对原始数据进行加工处理;
- 将处理后的数据发送出去。
上述功能并不复杂,但对于处理什么数据、如何加工处理、发送到哪里的需求大不相同,相互结合起来就有了众多的组合。为了使得整个Notification Agent更灵活更方便扩展。Ceilometer中采用了Pipeline的方式,简单的概括就是:
- 采用yaml格式的pipeline文件定义了每一个消息队列上的通知(notification)从收集到处理再到发送每一步的行为;
- 每一步的行为中通过一定的标识关联特定的处理插件;
- 针对每一个消息会按照pipeline的定义流过合适的插件,每个插件的输出是下一步插件的输入,就像工业生产中的流水线一样。
得益于pipeline的处理方式,每一步数据处理都可以以插件的形式存在,自由的组合,并且不需要关心其他插件的所作所为。这些相互独立功能单一的插件可以划分为三个类型,分别对应上述提到的三个需求:
-
Notification插件:监听消息队列上的某种通知数据;
-
Tranformer插件:将获得的通知数据,按pipeline定义做某种转化处理,这些处理可能是聚合,可能是形式转化,看一下官方的示意图:
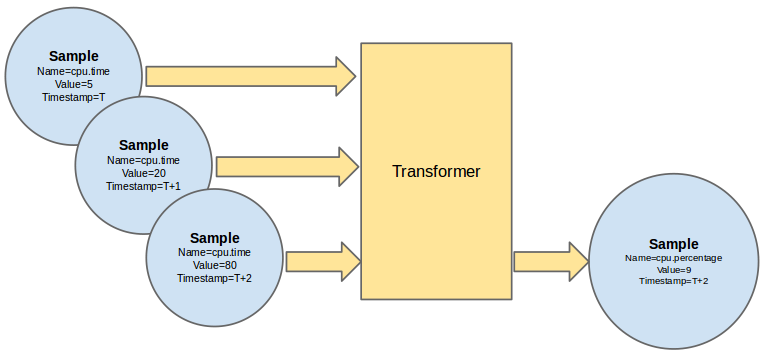
-
Publisher插件:将Tranformer处理后的数据发送到pipeline定义的地方。
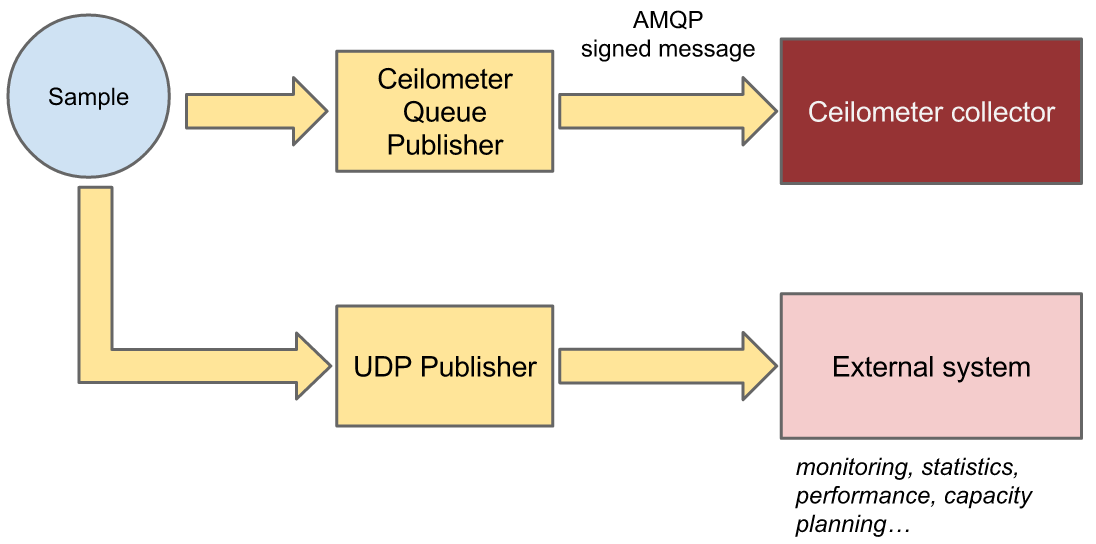
这些插件按对应的namespace定义在setpy.cfg配置文件中,并通过stevedore在运行时动态加载。
代码细节
了解了Notification Agent的整体结构和实现方式后,接下来从代码层面介绍其实现细节。
1. 入口
- Ceilometer采用pbr的方式管理配置;
- setup.cfg中定义了Notification Agent 入口位置,如下:
console_scripts =
ceilometer-agent-notification = ceilometer.cmd.eventlet.agent_notification:main
...
2. ceilometer.cmd.eventlet.agent_notification
相应的,在ceilometer/cmd/eventlet/agent_notification.py 文件中找到该启动函数,如下:
def main():
service.prepare_service()
os_service.launch(CONF, notification.NotificationService(),
workers=CONF.notification.workers).wait()
- prepare_service中做了一些初始化工作,如初始化日志,加载配置文件等;
- 第二句为核心,配置并启动了notification.NotificationService。
3. NotificationService 启动
ceilometer/notification.py 下找到NotificationService的启动部分代码,其中核心部分如下所示:
def start(self):
# pipeline及tranformer,publisher相关插件加载
self.pipeline_manager = pipeline.setup_pipeline()
...
# 设定并启动需要的消息队列listener
self._configure_main_queue_listeners(self.pipe_manager,
self.event_pipe_manager)
...
Notification Agent的主要工作,在上述两行代码中实现:
- pipeline.setup_pipeline中加载并解析了Notification Agent的灵魂pipeline,以及两种主要插件Transformer和Publisher;
- self._configure_main_queue_listeners中加载了Notification插件并注册启动了消息队列上的listener。
接下来分别进行介绍。
4. pipeline的加载
从pipeline.setup_pipeline()入手,通过代码的调用逻辑,一路找到了pipeline文件的加载代码,在PipelineManager的__init__方法中。对应一个pipeline.yaml示例来了解整个加载过程:
//pipeline文件示例
- name: disk_source
interval: 600
meters:
- "disk.read.bytes"
- "disk.read.requests"
- "disk.write.bytes"
- "disk.write.requests"
- "disk.device.read.bytes"
- "disk.device.read.requests"
- "disk.device.write.bytes"
- "disk.device.write.requests"
sinks:
- disk_sink
- name: network_source
interval: 600
meters:
- "network.incoming.bytes"
- "network.incoming.packets"
- "network.outgoing.bytes"
- "network.outgoing.packets"
sinks:
- network_sink
- name: disk_sink
transformers:
- name: "rate_of_change"
parameters:
source:
map_from:
name: "(disk\\.device|disk)\\.(read|write)\\.(bytes|requests)"
unit: "(B|request)"
target:
map_to:
name: "\\1.\\2.\\3.rate"
unit: "\\1/s"
type: "gauge"
publishers:
- notifier://
- name: network_sink
transformers:
...
publishers:
- notifier://
可以看出,pipe文件有两部分组成:
- “sources”中定义了当前过程所针对的数据类型(meter)以及要交给的目标sink;
- “sink”中定义了transformer和publisher过程;“transformers”的“name”属性对应于setpy.cfg中的Transformer插件,“publishers”下的url对应setpy.cfg中定义的Publisher插件。
class PipelineManager(object):
def __init__(self, cfg, transformer_manager, p_type=SAMPLE_TYPE):
self.pipelines = []
...
# 解析sources,封装为SampleSource
unique_names = set()
sources = []
for s in cfg.get('sources', []):
name = s.get('name')
if name in unique_names:
raise PipelineException("Duplicated source names: %s" %
name, self)
else:
unique_names.add(name)
sources.append(p_type['source'](s))
unique_names.clear()
# 解析sink,封装为SampleSink
sinks = {}
for s in cfg.get('sinks', []):
name = s.get('name')
if name in unique_names:
raise PipelineException("Duplicated sink names: %s" %
name, self)
else:
unique_names.add(name)
sinks[s['name']] = p_type['sink'](s, transformer_manager)
unique_names.clear()
# 将加载的SampleSource和SampleSink封装成SamplePipeline
for source in sources:
source.check_sinks(sinks)
for target in source.sinks:
pipe = p_type['pipeline'](source, sinks[target])
if pipe.name in unique_names:
raise PipelineException(
"Duplicate pipeline name: %s. Ensure pipeline"
" names are unique. (name is the source and sink"
" names combined)" % pipe.name, cfg)
else:
unique_names.add(pipe.name)
self.pipelines.append(pipe)
unique_names.clear()
上述PipelineManager的初始化函数中,做了以下操作:
- 将配置文件中所有sources,封装为SampleSource;
- 将配置文件中的所有sink,封装到SampleSink;
- 加载插件“ceilometer.publisher“ 到publishers,
- 加载插件“ceilometer.transformer” 到transformers;
- 将加载的SampleSource和SampleSink封装成SamplePipeline。
具体内容可以在Source, Sink, Pipeline的初始化函数中找到。
5. 监听消息队列
回到NotificationService,看_configure_main_queue_listeners函数中如何加载并监听消息队列。
def _configure_main_queue_listeners(self, pipe_manager,
event_pipe_manager):
# 加载Notification插件
notification_manager = self._get_notifications_manager(pipe_manager)
if not list(notification_manager):
LOG.warning(_('Failed to load any notification handlers for %s'),
self.NOTIFICATION_NAMESPACE)
...
# 调用Notification插件的get_targets函数获得所以要监听的target
endpoints = []
targets = []
for ext in notification_manager:
handler = ext.obj
if (cfg.CONF.notification.disable_non_metric_meters and
isinstance(handler, base.NonMetricNotificationBase)):
continue
for new_tar in handler.get_targets(cfg.CONF):
if new_tar not in targets:
targets.append(new_tar)
# 注册listener并启动
urls = cfg.CONF.notification.messaging_urls or [None]
for url in urls:
transport = messaging.get_transport(url)
listener = messaging.get_notification_listener(
transport, targets, endpoints)
listener.start()
- 首先在_get_notifications_manager中加载setup.cfg中的”ceilometer.notification”命名空间下的Notification插件;
- 调用插件的get_targets函数获得要监听的消息队列exchange和queue,更多关于消息队列内容见Rabbitmq;
- 注册消息队列上的listener并启动。会提供三个参数:
- transport:这里就是消息队列,
- targets:指定监听哪些exchange和queue,
- endpoints:Notification插件集合。
更多内容见:oslo.message Notification Listener。
6.Notification插件
完成上述的加载和启动后,整个Notification Agent就有条不紊的运行起来了,接下来我们看看各插件中的运行过程,首先来看Notification插件,该插件会监听消息队列上的某种通知。以插件Instance为例,该插件用来收集消息队列中的nova instance状态信息,其在setup.cfg中的注册信息如下:
ceilometer.notification =
instance = ceilometer.compute.notifications.instance:Instance
其处理过程如下:
- Instance初始化函数中用当前插件对应的event_type(这里是compute.instance.*),设置了self.filter_rule来注册当前的插件所需要的消息;
- 对应消息到来后会由其info方法接收消息;
- info会调用process_notification函数将从消息队列中收到的内容封装成Sample List;
def to_samples_and_publish(self, context, notification):
"""Return samples produced by *process_notification*.
Samples produced for the given notification.
:param context: Execution context from the service or RPC call
:param notification: The notification to process.
"""
with self.manager.publisher(context) as p:
p(list(self.process_notification(notification)))
-
对每一个sample调用PipelineManager的publisher;
在pipeline.py中
def publisher(self, context): """Build a new Publisher for these manager pipelines. :param context: The context. """ return PublishContext(context, self.pipelines)-
生成PublishContext,调用pipleline的publish_data方法,
def __enter__(self): def p(data): for p in self.pipelines: p.publish_data(self.context, data) return p def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback): for p in self.pipelines: p.flush(self.context)根据with语法,进入时会调用enter.
-
publish_data中调用SampleSink的publish_samples方法,
-
publish_samples中调用pipeline文件中定义的Transformer的handle_sample方法处理sample,
-
publish_samples中调用pipeline文件中定义的Publisher的publish_samples方法发送sample。
-
最后调用Transformer和Publisher相关函数的代码如下:
def _transform_sample(self, start, ctxt, sample):
try:
for transformer in self.transformers[start:]:
sample = transformer.handle_sample(ctxt, sample)
if not sample:
return
return sample
except Exception as err:
LOG.warning(...)
LOG.exception(err)
def _publish_samples(self, start, ctxt, samples):
# 调用Transformer的handle_sample处理sample
transformed_samples = []
if not self.transformers:
transformed_samples = samples
else:
for sample in samples:
sample = self._transform_sample(start, ctxt, sample)
if sample:
transformed_samples.append(sample)
# 调用Publisher的publish_samples发送对应sample
if transformed_samples:
for p in self.publishers:
try:
p.publish_samples(ctxt, transformed_samples)
except Exception:
LOG.exception(...)
7.Transformer插件
上面的介绍中有两个地方提到了负责数据格式转化的Transformer插件:
- 加载pipeline文件时对不同Transformer加载;
- 调用Transformer插件的publish_samples函数对数据进行数据转换。
下面看一下RateOfChangeTransformer,其在setup.cfg中的注册:
ceilometer.transformer =
rate_of_change = ceilometer.transformer.conversions:RateOfChangeTransformer
ceilometer/transformer/conversions.py中可以看到其代码实现如下:
def handle_sample(self, context, s):
"""Handle a sample, converting if necessary."""
key = s.name + s.resource_id
prev = self.cache.get(key)
timestamp = timeutils.parse_isotime(s.timestamp)
self.cache[key] = (s.volume, timestamp)
if prev:
prev_volume = prev[0]
prev_timestamp = prev[1]
time_delta = timeutils.delta_seconds(prev_timestamp, timestamp)
if time_delta < 0:
LOG.warn(_('dropping out of time order sample: %s'), (s,))
# Reset the cache to the newer sample.
self.cache[key] = prev
return None
volume_delta = (s.volume - prev_volume
if (prev_volume <= s.volume or
s.type != sample.TYPE_CUMULATIVE)
else s.volume)
rate_of_change = ((1.0 * volume_delta / time_delta)
if time_delta else 0.0)
s = self._convert(s, rate_of_change)
else:
LOG.warn(_('dropping sample with no predecessor: %s'),
(s,))
s = None
return s
8.Publisher插件
对于Publisher插件,同样地,在加载pipeline文件和发送数据时提到过。以向消息队列输出数据的SampleNotifierPublisher为例,pipeline中定义 “publishers: - notifier://“ 的sink会最终由该插件发送数据。其在配置文件中的注册信息如下:
ceilometer.publisher =
notifier = ceilometer.publisher.messaging:SampleNotifierPublisher
ceilometer/publisher/messaging.py中可以看到其代码实现如下:
class NotifierPublisher(MessagingPublisher):
def __init__(self, parsed_url, default_topic):
super(NotifierPublisher, self).__init__(parsed_url)
options = urlparse.parse_qs(parsed_url.query)
topic = options.get('topic', [default_topic])[-1]
self.notifier = oslo_messaging.Notifier(
messaging.get_transport(),
driver=cfg.CONF.publisher_notifier.telemetry_driver,
publisher_id='telemetry.publisher.%s' % cfg.CONF.host,
topic=topic,
retry=self.retry
)
def _send(self, context, event_type, data):
try:
self.notifier.sample(context.to_dict(), event_type=event_type,
payload=data)
except oslo_messaging.MessageDeliveryFailure as e:
raise_delivery_failure(e)
class SampleNotifierPublisher(NotifierPublisher):
def __init__(self, parsed_url):
super(SampleNotifierPublisher, self).__init__(
parsed_url, cfg.CONF.publisher_notifier.metering_topic) # metering_topic 默认值为metering
- 上述_send方法会被_publish_samples调用来发送数据;
- 可以看出最终的数据会被发到消息队列上,其topic为”metering.sample”,并通过sample方式发送。
9.Event 数据
需要指出的是,Notification Agent可以用两种方式处理监听到的数据,上面提到的是Sample方式,适用于处理数值数据。与之对应的Event方式则适合处理事件数据,如磁盘创建,实例删除。
- 通过配置notification.store_events可以控制是否开启Event方式;
- 与上述整套逻辑平行的,还有一套非常类似用来处理Event数据的逻辑;
- 对应的类为EventSource, EventSink, EventPipeline, EventNotifierPublisher等。
- 开关开启后会根据event_definitions.yaml中定义的监听任务生成event,并调用EventPipeline以及EventNotifierPublisher来处理
- 此时同一个event(例如虚拟机删除事件)会产生sample(因为sample endpoint)以及event(因为event endpoint),当然此事件必须在各自的endpoint中定义处理。
10.注意点
-
在polling中获取到的值会以以下方式发送 _send_notification(self, samples): self.manager.notifier.sample( self.manager.context.to_dict(), ‘telemetry.polling’, {‘samples’: samples} ) 在ceilometer.notification定义的处理类中对应于 _sample = ceilometer.telemetry.notifications:TelemetryIpc
-
meter = ceilometer.meter.notifications:ProcessMeterNotifications中处理的是通过mq消息队列中其他组件cinder、glance中发出的事件中获取sample,(nova的已经在instance中的notification做处理),具体的event定义在meter.yaml中定义 这样所有的sample统一由notification进行pipeline处理
参考
Github:Ceilometer Source Code
Ceilometer 源码学习 - Notification Agent(作者:catkang)